I know you’ve heard about the risks of an insecure website. But do you really know what a “Not Secure Website” means? Or why your browser shows a “Not secure” message next to some URLs?
- What “Not secure” means in your browser.
- How an insecure website puts your business and visitors at risk.
- Practical steps to fix a not secure website and protect your data.
In this post, we’ll walk through how to spot a not secure website, what it means for your visitors and your business, and the practical steps you can take to make sure your site is safe. We’ll also look at ways to ensure that your site is secure for your visitors.
What Does It Mean When Your Website Is Not Secure?
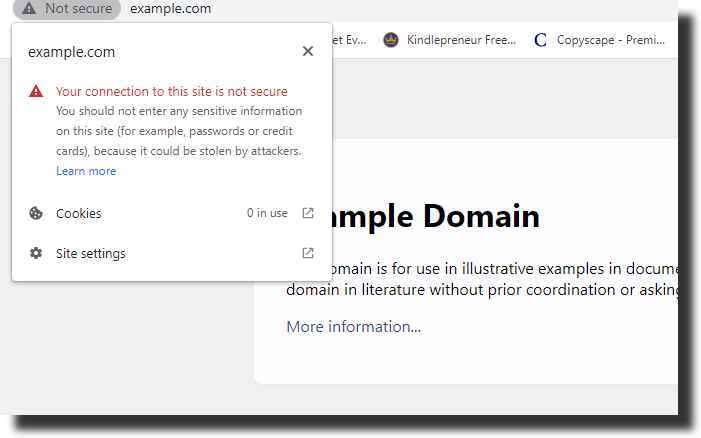
When you browse the web, modern browsers now show clear security labels in the address bar. If your site is marked “Not secure”, it means the connection between your visitor’s browser and your server is not protected.
This warning usually appears when the website does not use HTTPS. Your browser will either connect with a secure HTTPS protocol or an old HTTP protocol that sends data in plain text.

http:// (and not https://), the connection is not encrypted. Any data your visitors type can be intercepted – which is why browsers show the “Not secure” label.What Happens When Your Website Is Not Secure?
An unsecured website has serious consequences, especially for online shops and service businesses. Without proper protection, your site is more vulnerable to cyber-attacks and malware such as ransomware.
If your site is compromised:
- Attackers can change your pages, inject spam or malicious scripts;
- Visitors may be blocked by browser or antivirus warnings;
- Your site can be used to attack other websites or spread malware.
If you don’t secure your website, you put your customers’ data at risk. Cyber-attacks can damage your reputation, trigger chargebacks, or even lead to legal problems.
Studies show that visitors whose confidential information has been exposed are very unlikely to come back. For many small businesses, that can mean a permanent loss of customers and revenue.
What Is Website Security?
Website security is the set of measures and steps you take to secure your website from hackers, bots, and other cyber-threats. It’s not a one-time task. It’s a continuous process and an essential part of owning and running any site.
Why Is Web Security Important?
Nobody wants a hacked website. A single incident can:
- Take your site offline;
- Destroy months or years of SEO work;
- Expose sensitive customer data;
- Damage your brand in search results and on social media.
Security incidents can also result in lawsuits or regulatory penalties, especially if personal or payment data is involved. Investing in website security is much cheaper than dealing with the aftermath of a breach.
Why Do Websites Get Hacked?
There are now well over a billion websites online. This huge number gives attackers endless targets and lots of automation opportunities.
There are also many misconceptions about hacking. Some owners think their site is “too small” to attract any attention, so they ignore security. The reality is that most attacks are automated and don’t care about your brand size.
Attackers choose targets based on their goals:
- If they want large datasets, they go after bigger brands;
- If they want resources, spam, or a foothold, they often target smaller sites with weak protection.
Here are some common reasons websites get hacked:
- Steal information stored on the server;
- Exploit and redirect visitors;
- Abuse server resources for spam or bots;
- Manipulate search engines and crawlers;
- Pure vandalism or malice.
What Are the Most Common Website Threats and Vulnerabilities?
Here are some of the most common threats you should know about:
SQL Injections
SQL injection attacks work by injecting malicious code into vulnerable database queries. The attacker sends a specially crafted request, which changes the query so that it returns or modifies data in ways you never intended.
Through SQL injection, attackers can read, change, or delete data from your database, or even add new malicious content.
Credential Brute Force Attacks
One of the most common attack methods is simply guessing login details through automation.
Attackers program scripts that try thousands or millions of username–password combinations until one works. Once inside your admin panel, hosting panel, or SFTP server, they can do anything from sending spam to stealing card data.
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
Cross-site scripting injects malicious client-side scripts into a website and uses that site to spread the attack.
XSS allows the attacker to:
- Inject custom content into your pages;
- Change how your site looks or behaves;
- Make visitors’ browsers execute their code on page load.
If a logged-in administrator loads the infected page, the script may run with admin privileges, making a complete site takeover possible.
Website Malware Attacks and Infections
Once attackers gain unauthorized access, they can use your site in many ways:
- Inject SEO spam into your pages;
- Install backdoors to maintain access;
- Steal visitors’ credit card and personal data;
- Host botnet command-and-control scripts;
- Use visitors’ devices to mine crypto-currencies;
- Show unwanted ads or redirect to scam sites;
- Launch attacks on other websites;
- Host malicious downloads.
DoS/DDoS Attacks
A Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack overwhelms your site with fake traffic. The goal is to slow it down or make it completely unavailable.
The DDoS attacks are now a regular part of the website security landscape. Even a relatively small amount of traffic directed in the right way can cause serious disruption.
What is the Information Security CIA Triad?
The Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability (CIA) Triad is a classic model used to design security policies for organizations and websites.
-
Confidentiality
Confidentiality is about controlling who can access your information. Only people with the proper rights should see or manage your data.
This is enforced with usernames, passwords, multifactor authentication, and other access control tools.
-
Integrity
Integrity ensures that the information your users see is correct and unaltered. Encryption (for example, via SSL/TLS certificates) helps protect data from tampering while in transit.
-
Availability
Availability ensures that your website and its data are accessible when needed. DDoS attacks and server failures are common threats to availability.
How to Fix a Website That Is Not Secure?
Building a website is easier now thanks to content management systems like Joomla and WordPress.
But that also means you, as the site owner, are responsible for keeping it safe. Your users expect a secure experience whether your business is small or large. No method is perfect, so you need ongoing maintenance.
#1. Add an SSL Certificate and Use HTTPS
To secure your website, you must serve it over HTTPS, not HTTP.
HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) encrypts the connection between the browser and your server, protecting content from interception and tampering.

If your website asks visitors to register, sign in, or make a payment, HTTPS is non-negotiable.
What Is SSL?
SSL (now most commonly referred to as TLS) is the protocol that encrypts data between your website and your visitors’ browsers.
It ensures that information in transit cannot be read or changed by anyone without the proper keys.
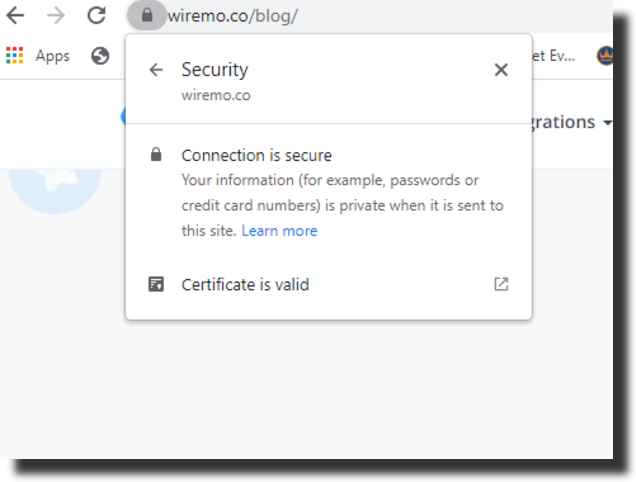
An example provider is GlobalSign, but there are many others, including free certificate authorities. Once installed and configured correctly, your site will show https:// in the URL bar and a padlock icon.
#2. Keep All Your Plugins and Software Current
Many security breaches happen because of old or vulnerable software. Attackers routinely scan the web for known weaknesses in outdated CMS versions, plugins, and themes.
Most platforms notify you when new versions are available. These releases often fix security issues. Don’t ignore them.
Some systems allow automatic installation of new versions, which is often the safest choice for non-technical owners.
The longer you leave old software running, the higher your risk. Keeping your stack current should be one of your top security habits.
#3. Use Smart, Strong Passwords
Most sites, tools, and services require passwords, and it’s tempting to reuse the same one everywhere. That’s a major risk.
If an attacker gets that password in one breach, they can try it on your CMS, hosting, email, and more.
Tips for Choosing a Secure Password
- Use a unique password for every login;
- Make it long (at least 12 characters) and random;
- Include numbers, symbols, and both upper- and lower-case letters;
- Avoid personal data (birthdays, names, pets, brands).
Store passwords in a secure password manager rather than in plain text files. Change them regularly, and never share them casually within your team.
#4. Use a Website Security Service
You can use free tools to detect common problems and monitor your site’s health. For example:
- SiteCheck – free scanner for malware and basic security issues;
- Google Search Console – security alerts plus search performance and traffic data.
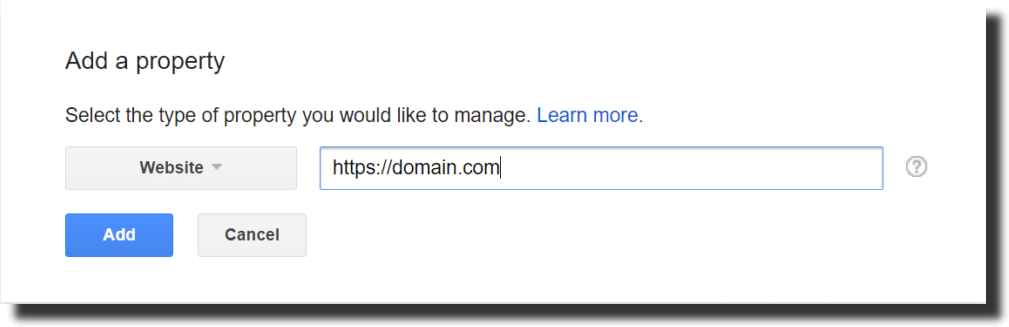
Adding HTTPS on Google Search Console:
- Best WAF – comparisons of cloud-based web application firewalls;
- Yandex Webmaster – search and security notifications.
#5. Choose a Secure Web Host
Your web host plays a huge role in security. Before you sign up, check what protections they provide.
Features to look for:
- Support for Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP);
- FTP for unknown users disabled by default;
- Regular automatic backups;
- Rootkit or malware scanning tools;
- Frequent security maintenance on their servers.
Pick a host that clearly explains how they protect customer sites and how they help you recover from incidents.
#6. Track Administrative and User Access Privileges
It’s normal to give employees, developers, or agencies access to your site. But every extra login is also an extra risk.
Before giving access:
- Check their experience with your CMS;
- Make sure they understand basic security practices;
- Give them only the permissions they need, not full control.
Keep a clear record of who has access, and remove old accounts when someone leaves your team.
#7. Change Your CMS Default Settings
Many attacks assume that your CMS is still using its default configuration.
As soon as you install your CMS, you should:
- Change default admin usernames;
- Adjust comment, registration, and permission settings;
- Review file permissions.
File Permission Basics
Each file can have permissions like:
- 'Execute' (1): run the program or script;
- 'Write' (2): change the file contents;
- 'Read' (4): view the file contents.
Combining these numbers sets the final permission. For example, 6 (2+4) means read + write.
There are also three user types:
- Owner – usually the creator of the file;
- Group – users in the same group;
- Public – everyone else.
Correctly configured permissions reduce the damage an attacker can do if they find a weakness.
#8. Know Your Web Server Configuration Files
Your web server configuration files live in the root of your website and control many key rules and behaviors.
Different servers use different files:
- Apache web servers: .htaccess;
- Nginx servers: nginx.conf;
- Microsoft IIS servers: web.config.
If you’re not sure what server you use, tools like SiteCheck can help you identify it and scan for common problems.
The more you know about your setup, the easier it becomes to lock it down and react quickly if something goes wrong.
#9. Ensure You Back Up Your Website
Backups are your safety net. If disaster strikes, a clean backup can save you from days or weeks of downtime.
There are many tools that can help you to recover your lost files.
Options include:
- Offsite backups with your host or a third-party service;
- Local copies on your own computer or external drives;
- Cloud backups for quick access from anywhere.
Tools like the BlogVault plugin can automate backups for WordPress sites.
Whatever you choose, make sure backups are:
- Automatic (scheduled);
- Stored in more than one place;
- Easy to restore in a real emergency.
#10. Use a Web Application Firewall
A Web Application Firewall (WAF) sits between your website and the internet. It inspects incoming traffic and blocks many types of attacks before they reach your server.
Cloud-based WAFs are easy to integrate, often via simple DNS or plugin changes, and can:
- Stop common exploits (SQL injection, XSS, etc.);
- Reduce malicious bot traffic;
- Help absorb some DDoS attacks.
#11. Take Care of Your Network Security
Your website might be safe, but your office network can still be a weak spot.
To reduce risks:
- Require password changes every few months;
- Set logins to expire after inactivity;
- Scan any device that connects to your network for malware.
#12. Install Monitoring and Scanning Tools
Monitoring the app or website regularly helps you spot unusual behavior early.
Set up:
- Security scans for malware and file changes;
- Alerts for failed logins, new admin users, or configuration changes;
- Monitoring on key pages and forms.
If you don’t use a WAF, make sure your manual checks are frequent.
#13. Apply Personal Security Best Practices
Your personal computer can become an entry point into your site.
A good website security guide will also remind you to scan your computer for malware if your website gets hacked.
Tips:
- Remove unused programs and browser extensions;
- Stick to trusted software sources;
- Limit the tools that have direct access to your website (FTP clients, editors, etc.).
What are Ecommerce Website Security and PCI compliance?
Ecommerce websites must follow Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS) rules when handling card payments.
Cardholder data includes:
- CVV digits;
- Service code;
- Full magnetic stripe data;
- Expiration date;
- Cardholder’s name.
For online stores, this data must:
- Be sent over HTTPS, never plain HTTP;
- Be stored securely or, ideally, not stored on your server at all;
- Be encrypted when passed to third-party processors.
Attackers actively target card data, both in transit and at rest, so PCI compliance is essential.
Web Security Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the importance of web security?
Web security keeps your visitors safe and your website online. Without it, hackers can steal data, take your site down, or use it for fraudulent activities. This can hurt your rankings, your reputation, and your revenue.
2. How can you tell that your website is not secure?
A secure website follows best practices, fixes known vulnerabilities, and often uses a website application firewall.
You can use tools like SiteCheck to look for malware, blacklist issues, or missing protection.
3. What are the common security risks for a website?
The most common security risks include weak access controls, insecure code, outdated plugins and themes, and resource abuse such as DDoS attacks. Many incidents start with something simple, like a weak password or old plugin.
4. Do I need security for my website?
Yes. Security is essential for every website, regardless of size. Hosting often provides only basic protection. You still need to manage your own CMS, extensions, passwords, and backups.
If you are not comfortable doing this yourself, pick a provider or partner who offers managed security services.
5. How can I secure my website?
You can:
- Use HTTPS with a valid SSL/TLS certificate;
- Install a website firewall;
- Keep your CMS, themes, and plugins on current versions;
- Use strong, unique passwords and limited admin access;
- Monitor your site for malware and suspicious changes.
6. Does "Not secure" mean my computer is infected?
No. The “Not secure” label refers to the website connection, not your device. It means data sent to that site isn’t properly protected. You should avoid entering sensitive information on such pages.
7. Do HTTP websites rank lower on Google?
Yes. Security is now a ranking factor. All else being equal, HTTPS sites have an advantage because search engines want to send users to safe pages.
Why Your Business Needs a Secure Website
You also need to understand how to keep it secure and protect your visitors’ data every single day.
An insecure site can lead to serious financial loss, lost traffic, and long-term damage to your brand. For e-commerce sites, it can also expose customers’ payment data.
Taking security seriously helps protect your visitors, your reputation, and your business.
Tags: not secure website, web security, website